- ABK Corel Draw AutoBackup
- ACL Corel Draw 6 keyboard accelerator
- ACM Used by Windows in the system directory
- ACP Microsoft Office Assistant Preview file
- ACT Microsoft Office Assistant Actor file
- ACV OS/2 drivers that compress and decompress audio data
- AD After Dark screensaver
- ADB Appointment database used by HP 100LX organizer
- ADD OS/2 adapter drivers used in the boot process
- ADM After Dark MultiModule screensaver
- ADP Used by FaxWorks to do setup for fax modem interaction
- ADR After Dark Randomizer screensaver
- AFM Adobe font metrics
- AF2 ABC Flowchart file
- AF3 ABC Flowchart file
- AI Adobe Illustrator drawing
- AIF Apple Mac AIFF sound
- ALB JASC Image Commander album
- ALL Arts & Letters Library
- AMS Velvert Studio music module (MOD) file
- ANC Canon Computer Pattern Maker file that is a selectable list of pattern colors
- ANI Animated Cursor
- ANS ANSI text
- API Application Program Interface file; used by Adobe Acrobat
- APR Lotus Approach 97 file
- APS Microsoft Visual C++ file
- ARC LH ARC (old version) compressed archive
- ARJ Robert Jung ARJ compressed archive
- ART Xara Studio drawing
- ART Canon Crayola art file
- ASA Microsoft Visual InterDev file
- ASC ASCII text
- ASD WinWord AutoSave
- ASM Assembler language source file
- ASP Active Server Page (an HTML file containing a Microsoft server-processed script)
- ASP Procomm Plus setup and connection script
- AST Claris Works "assistant" file
- ATT AT&T Group 4 bitmap
- AVI Microsoft Video for Windows movie
- AWD FaxView document
Friday, 30 September 2011
Alphabet A type of File Format
CPU
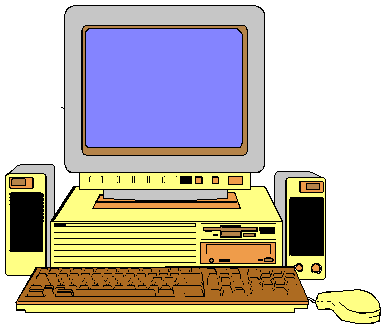 Parts of a computer
Parts of a computer
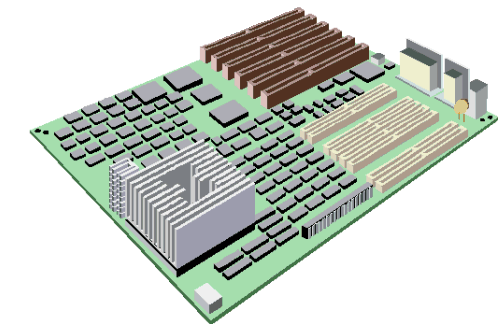 Everything inside the computer is connected to a circuit board called the 'motherboard'. The motherboard has sockets for low-level programming (BIOS), the computer's brain, called a CPU; the computer's memory (RAM, ROM and CMOS); and for add-on cards to control the video (picture), audio (sound), printer and anything else that might be connected to the computer. You may also find amodem inside on an add-on card. Everything inside the computer is connected to a circuit board called the 'motherboard'. The motherboard has sockets for low-level programming (BIOS), the computer's brain, called a CPU; the computer's memory (RAM, ROM and CMOS); and for add-on cards to control the video (picture), audio (sound), printer and anything else that might be connected to the computer. You may also find amodem inside on an add-on card. | |
 CPU: stands for 'Central Processing Unit' and is the 'brain' of the computer. Most CPU's today are made by Intel and bear such names as 'Pentium', 'Pentium Pro' and 'Pentium II'. Older Intel CPU's include the 80486 and 80386 families. Other manufacturers also make CPU's: Motorola for the Macintosh, AMD and Cirrus for PC's and others. The 'speed' of a CPU's processing is measured in megahertz. The CPU is the place that holds info about the operating system (DOS or Windows, for example). CPU: stands for 'Central Processing Unit' and is the 'brain' of the computer. Most CPU's today are made by Intel and bear such names as 'Pentium', 'Pentium Pro' and 'Pentium II'. Older Intel CPU's include the 80486 and 80386 families. Other manufacturers also make CPU's: Motorola for the Macintosh, AMD and Cirrus for PC's and others. The 'speed' of a CPU's processing is measured in megahertz. The CPU is the place that holds info about the operating system (DOS or Windows, for example). | |
 RAM: RAM is what you know as “Memory”, as in how much memory does your computer have? It is not permanent memory - the RAM is erased when the computer turns off. Permanent memory is stored on the hard drive. Memory is measured in increments of bits and bytes. Generally the least memory you should ever have with a Pentium computer is 64 MB (megabytes: look up kilo-, mega-, and giga- for more info), and more is much better. There are places on the motherboard (called “slots”) for memory modules. The memory modules are small printed circuit boards with memory chips on them and are usually either SIMM’s (Single Inline Memory Modules) or DIMM’s (Dual Inline Memory Module). RAM: RAM is what you know as “Memory”, as in how much memory does your computer have? It is not permanent memory - the RAM is erased when the computer turns off. Permanent memory is stored on the hard drive. Memory is measured in increments of bits and bytes. Generally the least memory you should ever have with a Pentium computer is 64 MB (megabytes: look up kilo-, mega-, and giga- for more info), and more is much better. There are places on the motherboard (called “slots”) for memory modules. The memory modules are small printed circuit boards with memory chips on them and are usually either SIMM’s (Single Inline Memory Modules) or DIMM’s (Dual Inline Memory Module).Don't confuse this with ROM. | |
 This is an add-in or expansion board such as a video card, sound card or modem. On every motherboard there are places to add circuit boards to extend the capabilities of the computer. The most common circuit boards used are the internal modem, sound card, and the video display adapter. There are various types of expansion slots that may be on the motherboard. The ISA (Industry Standards Association) expansion slot is the older type and most of the older circuit boards used this type of slot. A more sophisticated type of slot is the PCI and the newer modems, and more sophisticated sound cards require this type of slot. The newest type slot in a PC is the AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slot, which is specifically designed for a video display adapter. The AGP port enables high performance graphics capabilities, especially for 3D graphics. This is an add-in or expansion board such as a video card, sound card or modem. On every motherboard there are places to add circuit boards to extend the capabilities of the computer. The most common circuit boards used are the internal modem, sound card, and the video display adapter. There are various types of expansion slots that may be on the motherboard. The ISA (Industry Standards Association) expansion slot is the older type and most of the older circuit boards used this type of slot. A more sophisticated type of slot is the PCI and the newer modems, and more sophisticated sound cards require this type of slot. The newest type slot in a PC is the AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) slot, which is specifically designed for a video display adapter. The AGP port enables high performance graphics capabilities, especially for 3D graphics.The video card controls what you see on the monitor. It determines how many dots across the screen and down the screen the computer can look after. The more dots, the more information or the more detail you can see. The video card also controls how many colors you can see. Most computers today can show anywhere from 256 colors to many millions of colors. The sound card controls the sound. Most computers come with pretty cheap speakers, and the sound card can probably produce much better sound than the speakers can. With good speakers, today's sound cards can make your computer sound as good as a stereo! | |
 The hard drive uses disks that are made of aluminum or glass (and therefore 'hard'). Each disk can store much more information than either a floppy or CD-ROM. Sometimes, there may be several disks in a hard drive. However, the disks in a normal hard drive can not be removed or replaced. Today, hard drives are measured in gigabytes. That's one thousand million bytes. 1 gigabyte is about 11/3 CD-ROM disks. Sometimes a special cache is used for quick retrieval of often-used information (such as web pages). This is just a separate directory on the hard drive. The hard drive uses disks that are made of aluminum or glass (and therefore 'hard'). Each disk can store much more information than either a floppy or CD-ROM. Sometimes, there may be several disks in a hard drive. However, the disks in a normal hard drive can not be removed or replaced. Today, hard drives are measured in gigabytes. That's one thousand million bytes. 1 gigabyte is about 11/3 CD-ROM disks. Sometimes a special cache is used for quick retrieval of often-used information (such as web pages). This is just a separate directory on the hard drive. | |
 Generally when we talk about a floppy disk drive we are talking about the drive that uses the 3.5 inch 1.44Mb floppy disk in it. There have been other types that have come and gone. Generally when we talk about a floppy disk drive we are talking about the drive that uses the 3.5 inch 1.44Mb floppy disk in it. There have been other types that have come and gone. | |
 CD-ROM stands for Compact Disk – Read Only Memory. The original name was WORM drive, which meant Write Once Read Many. So the term CD-ROM is not really very accurate, but it is the name that has stuck. CD-ROM stands for Compact Disk – Read Only Memory. The original name was WORM drive, which meant Write Once Read Many. So the term CD-ROM is not really very accurate, but it is the name that has stuck. | |
 At one time there was the PC keyboard, the AT keyboard, and the 101 key enhanced keyboard, which had F9 through F12 keys and a separate numeric keypad. Now the 101 key enhanced keyboard is the standard type and keyboards are named according to the type of connection it makes to the computer. The two common types of connectors that go from the keyboard to the computer motherboard are the AT and the PS/2. The AT is the larger older type, and the PS/2 is a newer type and communicates better with he computer. At one time there was the PC keyboard, the AT keyboard, and the 101 key enhanced keyboard, which had F9 through F12 keys and a separate numeric keypad. Now the 101 key enhanced keyboard is the standard type and keyboards are named according to the type of connection it makes to the computer. The two common types of connectors that go from the keyboard to the computer motherboard are the AT and the PS/2. The AT is the larger older type, and the PS/2 is a newer type and communicates better with he computer. | |
There are a lot of varieties of mice in use today. Some have two buttons, some have 3 buttons, and some have a roller ball on top and don't require you to actually move the mouse on the desktop. There are also programmable mice, touch pads that substitute for a mouse, etc.. The standard types are the Serial, and the PS/2. The Serial mouse plugs into one of the 9 pin serial port of your computer (COM1), and the PS/2 mouse plugs into a special PS/2 port on your computer. | |
 A modem allows your computer to connect to another computer using the normal telephone line. It converts data from a computer format, which requires many wires, into a format that can be sent using only the two wires of a telephone line. At the other end of the telephone wires the process is reversed. Data transfer rates from the modem vary from 14.4Kbs to 56Kbs. (14.4Kbs, 28.8Kbs, 33.6Kbs, 56Kbs) There are special types of modems such as cable modems that can communicate at much higher data rates. A modem allows your computer to connect to another computer using the normal telephone line. It converts data from a computer format, which requires many wires, into a format that can be sent using only the two wires of a telephone line. At the other end of the telephone wires the process is reversed. Data transfer rates from the modem vary from 14.4Kbs to 56Kbs. (14.4Kbs, 28.8Kbs, 33.6Kbs, 56Kbs) There are special types of modems such as cable modems that can communicate at much higher data rates. | |
  The USB (Universal Serial Bus) connector is the newest type port (connector) on the PC. It is extremely easy to use. You just plug in a USB compatible device and the computer automatically configures itself to use the device. The computer does not have to be turned off or rebooted. As many as 127 USB peripherals can be plugged into a computer at one time. At 12Mbits per second it is more than 100 times as fast as a serial port. The next generation USB motherboards will communicate at 480Mbits per second. |
Thursday, 29 September 2011
First Web Browser page
the name of the first web browser
The first web browser ever written was called
"WorldWideWeb", and it was created by a man named Tim Berners-Lee.
While this was the very first web browser, it was not widely used, and was only
available for the NeXT platform.
The first widely-used web browser was Mosaic by Marc Andreessen and Eric Bina at the NCSA at the University of Illinois. The first version was written for X-Windows on Unix, and it was later ported to other operating systems.
Generation of Computer
First Generation (1941-1956)
Then in 1951 came the Universal Automatic Computer(UNIVAC I), designed by Remington rand and collectively owned by US census bureau and General Electric. UNIVAC amazingly predicted the winner of 1952, presidential elections, Dwight D. Eisenhower.
In first generation computers, the operating instructions or programs were specifically built for the task for which computer was manufactured. The Machine language was the only way to tell these machines to perform the operations. There was great difficulty to program these computers ,and more when there were some malfunctions. First Generation computers used Vacuum tubes and magnetic drums(for data storage).
| vacuum tube |
 |
| first computer |
 |
| ENIAC |
The invention of Transistors marked the start of the second generation. These transistors took place of the vacuum tubes used in the first generation computers. First large scale machines were made using these technologies to meet the requirements of atomic energy laboratories. One of the other benefits to the programming group was that the second generation replaced Machine language with the assembly language. Even though complex in itself Assemly language was much easier than the binary code.
Second generation computers also started showing the characteristics of modern day computers with utilities such as printers, disk storage and operating systems. Many financial information was processed using these computers.
In Second Generation computers, the instructions(program) could be stored inside the computer's memory. High-level languages such as COBOL (Common Business-Oriented Language) and FORTRAN (Formula Translator) were used, and they are still used for some applications nowdays.
Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
Although transistors were great deal of improvement over the vacuum tubes, they generated heat and damaged the sensitive areas of the computer. The Intergreated Circuit(IC) was invented in 1958 by Jack Kilby. It combined electronic components onto a small silicon disc, made from quartz. More advancement made possible the fitings of even more components on a small chip or a semi conductor. Also in third generation computers, the operating systems allowed the machines to run many different applications. These applications were monitored and coordinated by the computer's memory.
Fourth Generation computers are the modern day computers. The Size started to go down with the improvement in the integerated circuits. Very Large Scale(VLSI) and Ultra Large scale(ULSI) ensured that millions of components could be fit into a small chip. It reduced the size and price of the computers at the same time increasing power, efficiency and reliability. "The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, took the integrated circuit one step further by locating all the components of a computer (central processing unit, memory, and input and output controls) on a minuscule chip."
Due to the reduction of cost and the availability of the computers power at a small place allowed everyday user to benefit. First came the minicomputers, which offered users different applications, most famous of these the word processors and spreadsheets, which could be used by non-technical users. Video game systems like Atari 2600 generated the interest of general populace in the computers.
In 1981, IBM introduced personal computers for home and office use. "The number of personal computers in use more than doubled from 2 million in 1981 to 5.5 million in 1982. Ten years later, 65 million PCs were being used." Computer size kept getting reduced during the years. It went down from Desktop to laptops to Palmtops. Machintosh introduecd Graphic User Interface in which the users didnt' have to type instructions but could use Mouse for the purpose.
The continued improvement allowed the networking of computers for the sharing of data. Local Area Networks(LAN) and Wide Area Network(WAN), were potential benefits, in that they could be implemented in corporations and everybody could share data over it. Soon the internet aand World Wide Web appeared on the computer scene and formented the Hi-Tech revolution of 90's.
 |
| Add caption |
Fifth generations computers are only in the minds of advance research scientiets and being tested out in the laboratories. These computers will be under Artifical Intelligence(AI), They will be able to take commands in a audio visual way and carry out instructions. Many of the operations which requires low human intelligence will be perfomed by these computers.
Parallel Processing is coming and showing the possibiliy that the power of many CPU's can be used side by side, and computers will be more powerful than thoes under central processing. Advances in Super Conductor technology will greatly improve the speed of information traffic. Future looks bright for the computers.
Wednesday, 28 September 2011
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)


















